Your Planets
Portraits of the Planets
Aspects between Planets
The planetary ages
The planetary families
Planets in Signs
The Planets in comics


Variations of sunrise, Sun’s culmination and sunset throughout the zodiacal year. The Sun’s yearly apparent trajectory (ecliptic) is displayed. Simulation created with the Stellarium freeware. Simulated observation from the 45th parallel north, located halfway between the Earth’s equator and the North Pole. This corresponds to the following regions: southern France, northern Italy, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, southern Russia, northern China, northern Japan, northern United States, southern Canada.
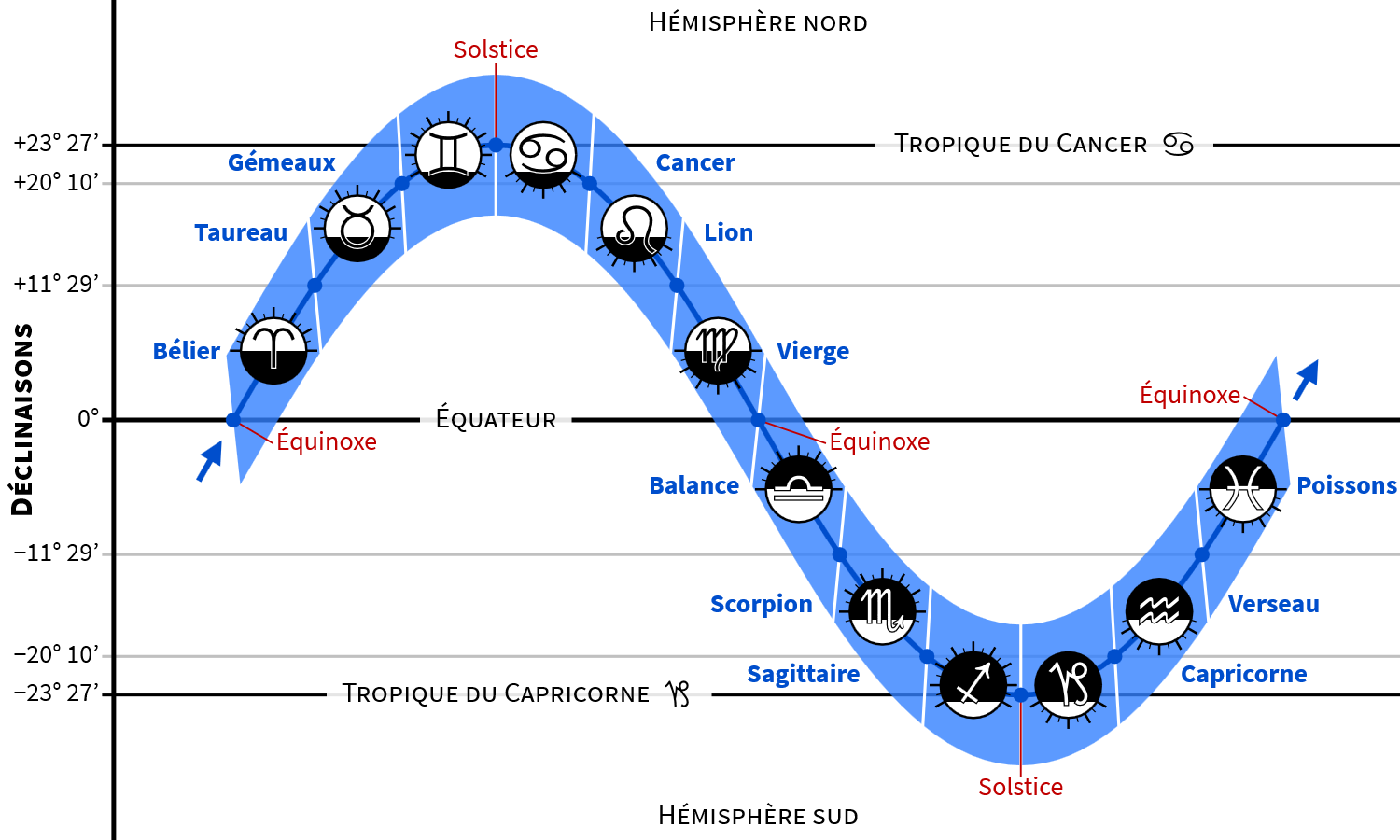
▶ the Sun leaves the ecliptic sector of Pisces and enters Aries. It is then vertical to the Earth’s equator.
▶ everywhere on Earth, the Sun rises in the east and sets in the west, while the lengths of days and nights are practically equal (12 hours each).
▶ throughout the northern hemisphere it is the time of the year when the days increase the fastest while the nights decrease the fastest. For six months until September equinox, the days will be longer than the nights.
▶ seen from the 45th parallel north, when facing due south in the early afternoon, the Sun culminates at about 45° above the horizon.
▶ the Sun leaves the ecliptic sector of Gemini and enters Cancer. It is then vertical to the Tropic of Cancer (at about 23° north latitude).
▶ throughout the northern hemisphere it is the longest day and the shortest night of the year. The Sun rises in the northeast and sets in the northwest. For six months until December solstice, the days will get shorter and shorter while the nights will get longer and longer.
▶ seen from the 45th parallel north, the visible trajectory of the Sun lasts about 15 hours. When facing due south in the early afternoon, the Sun culminates at about 68° above the horizon.
▶ the Sun leaves the ecliptic sector of Virgo and enters Libra. It is then vertical to the Earth’s equator.
▶ everywhere on Earth, the Sun rises in the east and sets in the west, while the lengths of days and nights are practically equal (12 hours each).
▶ throughout the northern hemisphere it is the time of the year when the days decrease the fastest while the nights increase the fastest. For six months until March equinox, the days will be shorter than the nights.
▶ seen from the 45th parallel north, when facing due south in the early afternoon, the Sun culminates at about 45° above the horizon.
▶ the Sun leaves the ecliptic sector of Sagittarius and enters Capricorn. It is then vertical to the Tropic of Capricorn (at about 23° south latitude).
▶ throughout the northern hemisphere it is the shortest day and the longest night of the year. The Sun rises in the southeast and sets in the southwest. For six months until June solstice, the days will get longer and longer while the nights will get shorter and shorter.
▶ seen from the 45th parallel north, the visible trajectory of the Sun lasts about 9 hours. When facing due south in the early afternoon, the Sun culminates at about 22° above the horizon.
▶ The astronomical reality of the zodiac
▶ Your zodiac Sign
▶ Signs and seasons
▶ Planetary trios in Signs
▶ The zodiac and the precession of the equinoxes
▶ Zodiac Signs & constellations: videos
▶ The human reflexology zodiac
▶ Autour du zodiaque : de l’eau dans un Signe de Feu ?
▶ Zodiaque et sphère locale
▶ Mythologie du zodiaque
▶ Zodiaque et formes de l’inhibition
▶ Do we change character by changing Sun sign?
▶ Énergie-Espace-Temps-Structure et zodiaque
▶ Genèse du zodiaque conditionaliste
▶ L’horloge photopériodique du genou
▶ Sun Sign and Rising Sign
▶ Astrologie, adaptation & inadaptation
▶ Les rythmes du zodiaque
▶ Simplified cosmography of the solar system
▶ Thème de domitude et hiérarchisation planétaire
▶ Effets et contre-effets des images et représentations sur les faits et les idées
▶ Le taijitu dans le système solaire
▶ Zodiac, planets and Jungian typology

Le grand livre du zodiaque
par
180 pages. Illustrations en couleur.
Ce livre présente et explique les trois zodiaques : celui du décor des constellations, celui de l’astrologie traditionnelle basé sur les Quatre Éléments symboliques (Feu, Terre, Air & Eau) et celui de l’astrologie naturelle basé sur les phénomènes astronomiques objectifs.
Téléchargez-le dès maintenant dans notre boutique